Clients often ask us: "Which is better for my project – a proxy or a VPN?". We always answer that these tools solve different problems, and in the modern internet, the boundaries between them are blurring thanks to new technologies. In this article, we will break down the technical differences, debunk popular myths, and help you choose a reliable solution for a stable and uninterrupted connection.
How does a proxy work and what are its features?
A proxy — is an intermediary (an additional link) between the user and the destination server. Its task: to receive your request, replace the IP address, and send the data to the site on its own behalf. The operation algorithm is as follows:
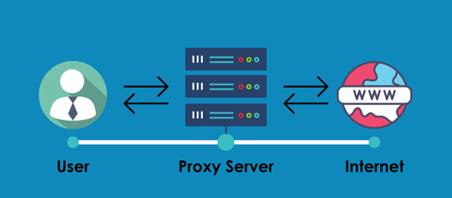
Fig. 1. Proxy operation scheme.
- The user sends a request to the proxy server.
- The proxy forwards this request to the internet (your real IP is hidden).
- The website sends a response back to the proxy.
- The proxy returns the data to you.
Proxies operate at layers 5-7 of the OSI model (Session, Presentation, and Application). This means they operate on data at the level of specific applications or protocols (HTTP, FTP, etc.).
Important nuances of encryption and operation
HTTP-proxy. They operate at the application level (OSI layer 7). They are excellent for browsers and software using HTTP requests. They can cache data (save copies of images or pages), which sometimes speeds up loading, but this is an optional feature.
SOCKS5-proxy. They operate at the session level (OSI layer 5). They are more versatile: they transmit any traffic (TCP/UDP) without interfering with it. Suitable for messengers, games, and torrents.
The encryption myth: It is often said that proxies do not encrypt data. This is only partially true. A proxy does not guarantee encryption of the channel from you to the proxy server itself (unlike a VPN). However, if you access a site with HTTPS, your data (passwords, cards) is encrypted by the browser before being sent, and the proxy server will only see the domain you are visiting, but not the contents of the packets.
The ping and speed myth: A proxy — is one additional hop (node) in the network. Contrary to popular belief, adding an extra node usually increases latency rather than decreasing it. Low ping is only possible if the proxy server is geographically close to the target resource (e.g., a game server) and has a better route than your ISP. Proxy speed depends on its location, channel load, and hardware power.
Warning! The danger of free proxies.
Public (free) proxies — are a trap. The owner of such a server can log your traffic, intercept unencrypted data (cookies, passwords from HTTP sites), replace content (inject their own ads), or use your device as part of a botnet. We strongly recommend using proxies only from reliable paid sources.
In which projects are proxies used?
High-quality private proxies — are the standard for professional work where mass scale or imitation of a real user is required.
- Web scraping and parsing. Collecting analytical data on prices and competitors with high connection stability.
- Traffic arbitrage and profile management. Working with professional marketing accounts on Facebook, Google, TikTok via specialized browsers.
- Secure access. Users create isolated profiles to ensure privacy and secure access to content while complying with platform rules.
- SMM automation. Effective management of marketing campaigns on social networks.
- Ad testing. Checking content display across different geos.
- Gaming. A proxy masks your real IP address, allowing access to game servers from different regions. A quality connection ensures stable gameplay without lags and, in some cases, helps reduce ping by optimizing the route.
What is a VPN and why do websites "see" it?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and the server. The level of the OSI model at which a VPN operates is determined by its protocol. IPsec — is a classic representative of layer 3 (Network), working with IP addresses. If direct physical connection between devices needs to be simulated, layer 2 protocols such as L2TP or PPTP are used. Meanwhile, OpenVPN stands apart: it wraps traffic in SSL/TLS (like regular web traffic), operating at the application level (7), but simultaneously creates virtual interfaces for layers 2 and 3. In TUN mode — it is layer 3 (Network, like IPsec), and in TAP mode — it is layer 2 (Data Link, for Ethernet emulation).
VPN operation algorithm
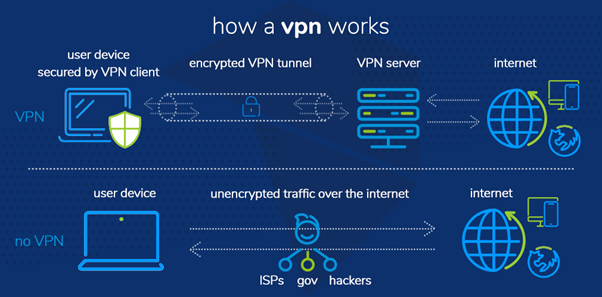
Fig. 2. VPN operation scheme.
Initiation: You send a request (for example, opening a page in a browser).
Local encryption: The VPN client on your device instantly encrypts the data, turning it into unreadable code for the ISP.
Tunneling: The encrypted packet is transmitted through a secure tunnel to a remote VPN server.
Anonymization and exit: The VPN server decrypts the data, replaces your IP address with its own, and forwards the request to the destination site.
Resource response: The site processes the request and sends the response back to the VPN server (unaware of your real address).
Reverse protection: The VPN server encrypts the received response again and sends it to your device.
Decryption: The client on the device decrypts the data, and you gain access to the content.
The main problem with regular VPNs
A classic VPN is great for protecting against a hacker neighbor in a cafe with Wi-Fi, but it is poorly suited for accessing resources with strict geo-policies.
The fact is that 99% of VPN services use Data Center IP addresses. These addresses are present in public databases. Streaming services, financial platforms, and social networks can detect VPN usage and request additional verification.
Furthermore, regular VPN protocols (OpenVPN, WireGuard) have specific "digital fingerprints" that are easily analyzed by traffic monitoring systems.
Evolution: VLESS/XRAY and Mobile proxies
What should you do if you need the convenience of a VPN (toggle one button on your phone) but the anonymity and "trust" of mobile proxies? Use modern protocols.
We offer solutions based on VLESS/XRAY with XTLS-Reality support, running over mobile proxies. This provides unique advantages:
- High level of anonymity. Your traffic looks like regular web browsing; it does not raise suspicion from ISPs.
- High trust. You access the network from the IP address of a real mobile operator, not a spammed data center.
- Convenience. It works like a VPN (via an app) but with the quality of elite proxies.
You can check the rates for Mobile proxies with Vless/Xray and the next-generation VPN here.
Comparison: Proxy, Regular VPN, and VPN+Proxy (Vless/Xray)
| Aspect | Proxy (Datacenter/Residential/Mobile) | Regular VPN | VPN + Proxy (VLESS/Mobile) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Level | Application / Browser (setup separately). | Entire system (one button). | Entire system or selective (Routing). |
| Encryption | Depends on protocol (HTTPS encrypts Payload). | Full tunnel encryption. | Full encryption + masking as regular traffic. |
| Network Trust Level | High (if mobile proxy), Medium (if residential), Regular (if server-based). | Low (Data center IPs are often public). | Maximum (you look like a regular mobile subscriber). |
| Best For | Scraping, automation software, working in professional browsers. | Changing country for YouTube, protection on public Wi-Fi, simple websites. | Online gaming, access to international platforms, Mobile arbitrage, working with resources with strict geo-restrictions. |
Summary: what to choose?
- Use a Proxy if you are a professional: you need to manage multiple accounts, parse data, or work through specialized software (automation tools, multi-login browsers).
- Use a Regular VPN if your goal is simple everyday anonymity: hiding history from your ISP or safely browsing in a cafe.
- Use a combination of VPN + Mobile proxies (VLESS/XRAY) if you work with demanding services (financial platforms, crypto exchanges) that require a high-quality residential IP. This is the golden mean, providing maximum protection and a "clean" IP address.
High-quality Server, Residential, and Mobile proxies, as well as configured VLESS setups, can always be found in the CyberYozh App catalog.
